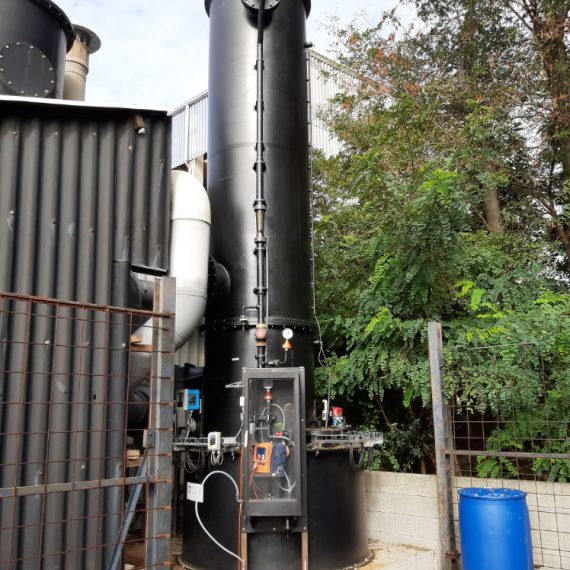
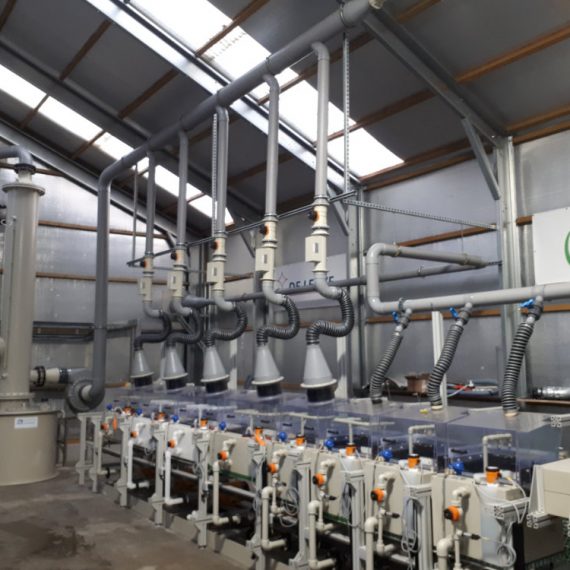
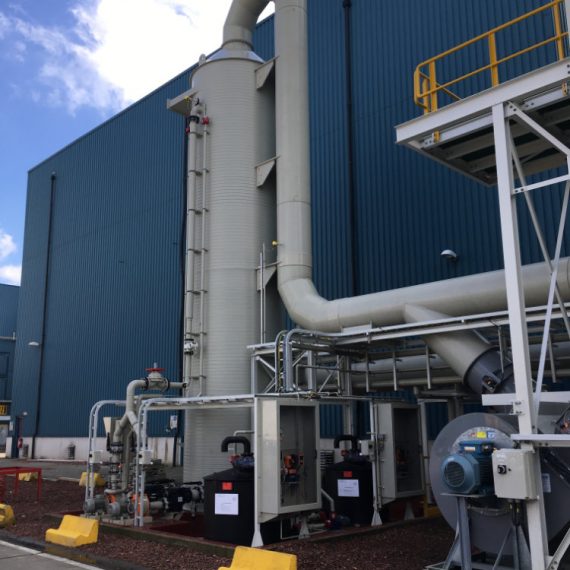
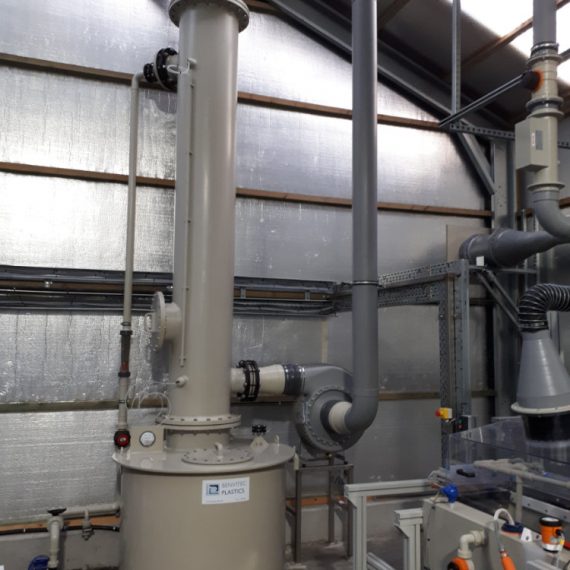
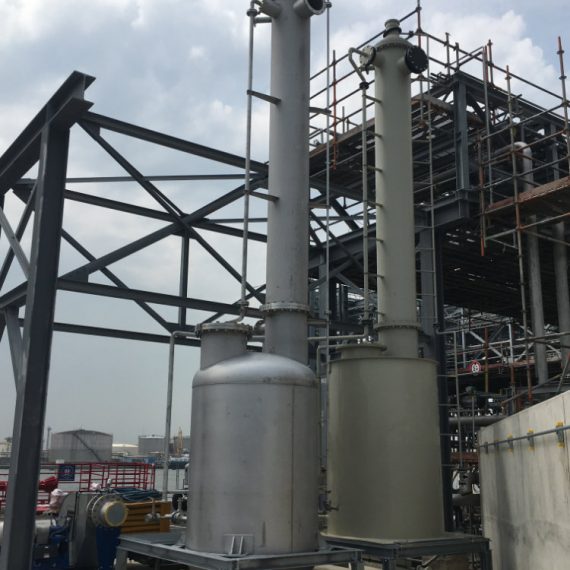
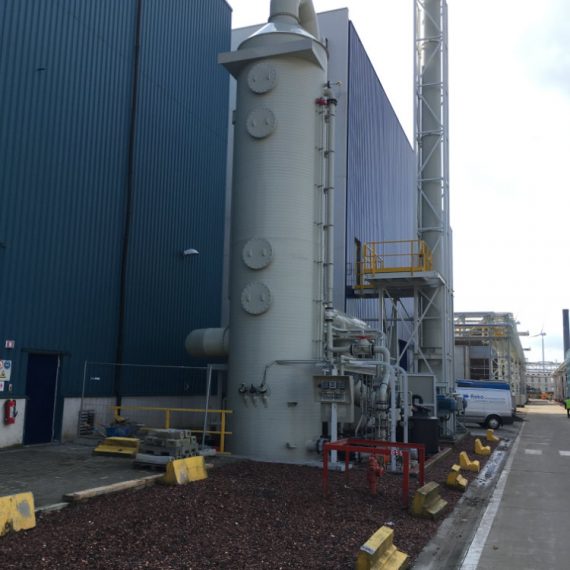
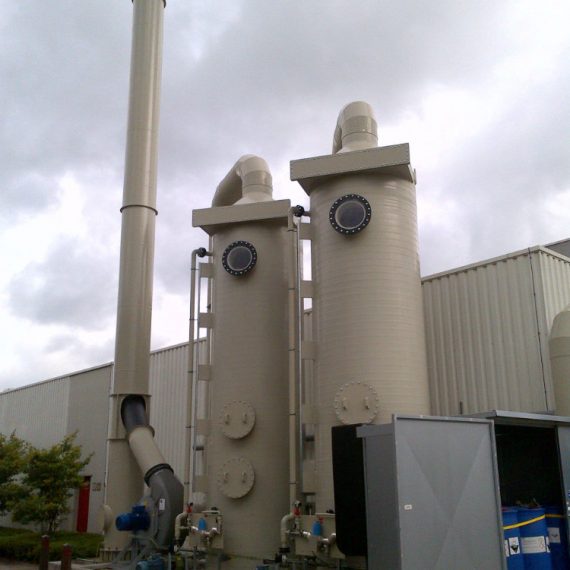
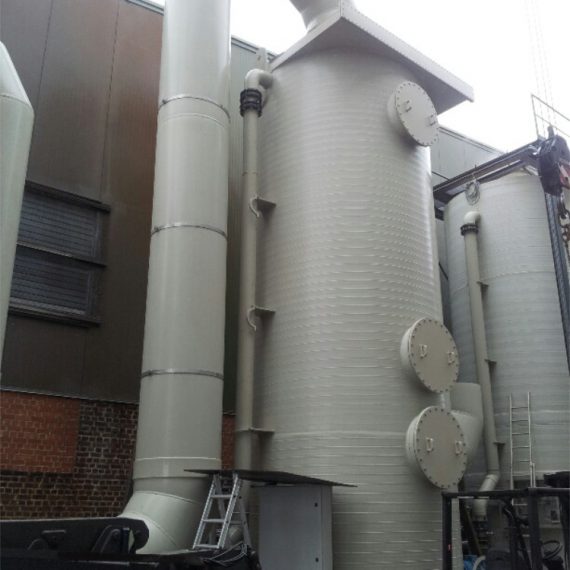
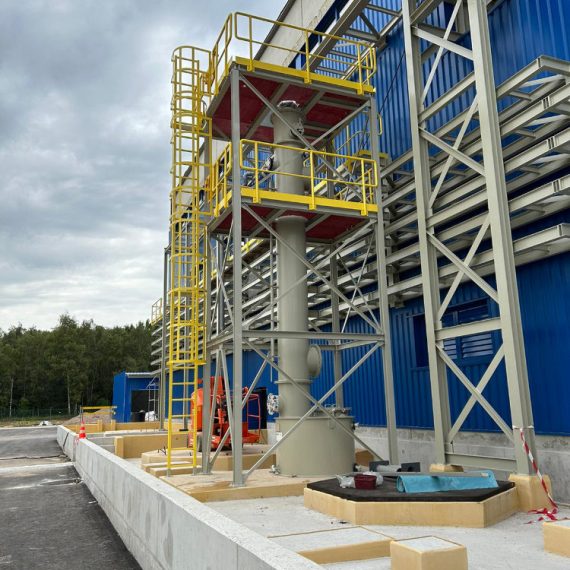
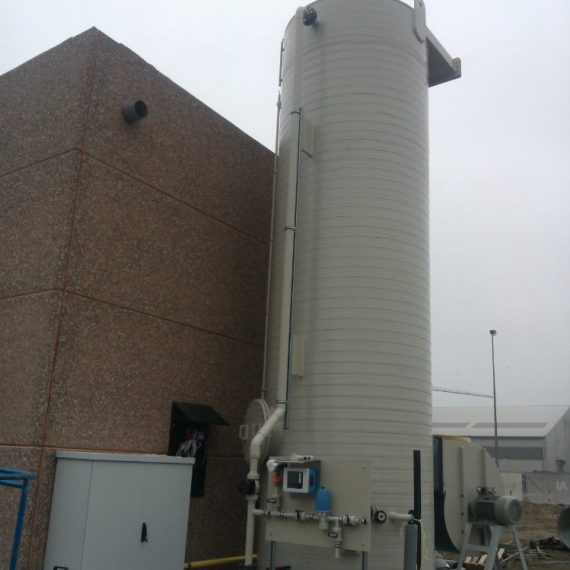
About Factory
Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique ore senectus et netus pellentesques Tesque habitant.
Follow Us On Social
[social_icons type="square_social" icon="fa-linkedin" use_custom_size="yes" custom_size="13" custom_shape_size="14" link="https://www.linkedin.com/company/qode-themes/" target="_blank" border_radius="4" icon_color="#ffffff" icon_hover_color="#ffffff" background_color="#5a5959" background_hover_color="#fab012" background_color_transparency="1" border_width="0"][social_icons type="square_social" icon="fa-facebook" use_custom_size="yes" custom_size="13" custom_shape_size="14" link="https://www.facebook.com/qodeinteractive" target="_blank" border_radius="4" icon_color="#ffffff" icon_hover_color="#ffffff" background_color="#5a5959" background_hover_color="#fab012" background_color_transparency="1" border_width="0"][social_icons type="square_social" icon="fa-twitter" use_custom_size="yes" custom_size="13" custom_shape_size="14" link="https://twitter.com/qodeinteractive" target="_blank" border_radius="4" icon_color="#ffffff" icon_hover_color="#ffffff" background_color="#5a5959" background_hover_color="#fab012" background_color_transparency="1" border_width="0"]